The Resurgence of Heat Pumps in US Homes: Explore Now

Many large HVAC systems have gradually made their way into commercial and residential settings as people's understanding of the various types of sustainable technology available on the market has grown, with heat pumps being the preferred option for many. Read on to know what is a heat pump system and types of heat pumps.
What is a heat pump?
A heat pump is a component of a heating and cooling system which is installed outside your home. It can chill your house like a central air conditioner, but it can also generate heat. A heat pump carries heat from the cold external air to your home during the winter months, and during the warmer months, it removes heat from the inside air to cool your house. Heat pumps keep your homes warm and cool throughout the year by using refrigerant, which is driven by electricity. Homeowners may not need to build separate heating systems because they can manage both cooling and heating using heat pumps.
Heat pump water heaters
Heat pumps are typically used by homeowners to heat and cool their houses. However, a heat pump can also be used to heat water, either as a separate water heating system or as a system that combines space conditioning and water heating.
Instead of producing heat directly, heat pump water heaters transport heat from one location to another using electricity. They can therefore be two to three times more energy-efficient than standard electric resistance water heaters.
How does a heat pump work?
A heat pump is an electrically powered device that transports heat from a source of low temperature to a location with a greater temperature, which is referred as a sink.
Heat flows naturally from high temperatures in one region and to places of low temperatures. A heat pump transfers the energy present in a colder location to a warmer one by using additional electrical energy to counteract the natural flow of heat.
The temperature of a source decreases as energy is removed from it. Thermal energy will be taken from the home if it is the source, cooling this area. The cooling mode of a heat pump works on the same basis as air conditioners and refrigerators. Similar to this, a sink's temperature rises when energy is applied to it. Thermal energy will be added if the house is used as a sink, heating the area. Because a heat pump is totally reversible, it can comfortably heat and cool your house all year round.
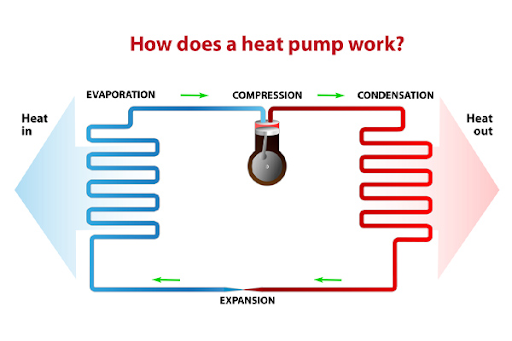
(Image source: https://www.townsendtotalenergy.com)
What are the main components of a heat pump?
Although people may be familiar with the various heat pump variants, such as ground source and air source heat pumps, when it comes to these effective HVAC systems. However, many people might not be aware of the importance of comprehending the various components of a heat pump.
The heat pump is comprised of a main pump, evaporator, condenser, compression parts, and expansion valve. We offer a wide range of high-quality heat pump parts for the best prices. Browse through our collection if you are looking for one.
- Main pump: The main pump is the most significant part of this sustainable technology, whether it be a ground source heat pump (GSHP) or an air source heat pump (ASHP), and here is where everything happens.
For the heating system to start functioning, heat absorption from the ground or the air is necessary. This acquired heat is subsequently transferred to other parts of the pump, including the refrigerant, and utilized to heat your house.
Even if the procedure is typically automated, you still need to be sure to regularly check on its maintenance. Regular inspections are necessary to ensure that the main heat pump remains in good operating order, from problems with the outside fan to the pump itself running nonstop.
If you’re looking to replace your old heat pump PartsHnc is the place to find new heat pumps.
- Evaporator: The evaporator in a heat pump is a low thermal exchanger. The refrigerant enters the evaporator as a liquid, which evaporates to produce a low-temperature vapor after absorbing heat from the heat source.
The expansion valve and compressor's suction force transform the refrigerant from a liquid to a gas. The evaporator gets cold as a result and has a tendency to absorb heat from the surroundings because this demands a lot of heat.
However, it is one of the most crucial parts of a heat pump because of its function in altering the form of the liquid or gas.
- Condenser: The condenser is an exterior part of the heat pump which gathers or releases heat according to the outside temperature. In order to transmit heat quickly, it is typically made of copper tubing with aluminum fins as well as complete aluminum tubing.
The refrigerant enters the condenser as high-temperature gas, and it exits as a high-temperature liquid.
To help with heat transfer, the condenser fan then moves air over the coils.
The refrigerant is then pushed across the coils under pressure. However, you must remember that obstructions or blockages from the outside can harm the condenser.
This is where replacing the old part entirely with a new condenser will prove to be efficient when you have a broken heat pump. PartsHnC offers condensers from various manufacturers for competitive prices.
- Compression and expansion valve: The compressor transforms the low temperature, low pressure gas into a high temperature, high pressure gas. The liquid changes from a liquid to a gas and back again due to the low and high pressure it generates.
The expansion valve, which modifies the pressure and temperature for the heat pump, transports the high-pressure refrigerant liquid from the condenser.
To adequately provide enough heat for your house or commercial property, a heat pump's various components must all function effectively in a continuous cycle.
Top Selling Products
What is the difference between a heat pump and HVAC?
The main distinction between the two HVAC systems is that an air conditioner cannot both heat and chill space while a heat pump can do both.
In order to provide heat during the chilly months, an air conditioner is frequently combined with a furnace. An entire heating and cooling system are made up of a furnace and an air conditioner in regular HVAC systems.
Types of heat pumps
There are three basic types of heat pumps that are connected by ducts: air-to-air, water-source, and geothermal heat pumps. They gather heat outside your home from the air, water, or earth and compress it for use inside.
a) Air source heat pump
The air-source heat pump, which exchanges heat between your home and the outside air, is the most popular form of a heat pump. Relative to electric resistance heating, such as furnaces and baseboard heaters, a modern heat pump can cut your energy use for heating by about 50%.
Air-source heat pumps are also manufactured as ductless mini-split heat pumps for homes without ducts. Additionally, a unique kind of air-source heat pump known as a "reverse cycle chiller" produces hot and cold water instead of air, enabling it to be used in heating mode with radiant floor heating systems.
b) Geothermal heat pump
By transporting heat between your home and the earth or a local water source, geothermal (ground-source or water-source) heat pumps are able to operate more efficiently. Geothermal heat pumps use generally stable ground or water temperatures, which lowers running costs despite their higher initial cost.
They can control humidity, consume 50%–60% less energy, are dependable and strong, and fit in a wide range of spaces. The size of the space, the subsoil, and the surrounding environment will determine if a geothermal heat pump is suitable for you.
c) Water source heat pumps
Heat is released by water instead of air in water source heat pumps. They are less common and require access to a water reservoir, well, or other water supply.
In addition to these main types, there are a few sub-types of heat pump systems available to boost efficiency.
- Hybrid Heat Pump (combination of ground & air source heat pump; a combination of heat pump and gas/oil boiler)
- Solar Heat Pump
- Absorption or Gas-Fired Heat Pump
Are heat pumps good?
In terms of enhancing indoor comfort, heat pumps are more adaptable because they can both operate as air conditioners and heaters depending on the season. This implies that those who live in warmer areas can simply use a heat pump system to heat and cool their homes.
Heat pump vs furnace
While heat pumps use electricity to pull heat from the outside air and transfer it indoors, furnaces burn oil or gas to produce heat. Heat pumps function better in warmer places than furnaces because of how they produce less heat.
It is challenging to compare the energy efficiency of heat pump systems and gas furnaces. A highly efficient natural gas furnace can provide up to 99% efficiency in heating homes. When compared to gas furnaces, high efficiency heat pumps often utilize less source energy in warmer climes. However, gas furnaces that are 95% efficient perform better than ENERGY STAR® heat pumps in colder areas.
You must factor in installation costs when choosing an oil furnace. An air handler and an outside unit are both necessary for a heat pump. You should also compare the price of heating oil to the price of electricity. High efficiency heat pumps can be a very useful and efficient solution in moderately hot weather. An oil furnace may be able to give dependable warmth in colder climates even when the temperature drops well below freezing.
The biggest similarity between the electric furnace and heat pump is they both use electricity to heat your home. And, both are more prevalent in places where winters are milder. While heat pumps use electricity to transfer heating energy from the outside to the inside, electric furnaces use electric coils to produce heat.
Despite being 100% energy efficient, electric furnaces can actually cost nearly double the times as much as a standard heat pump to provide the same quantity of heat. A heat pump system also offers cooling in addition to heating. During the summer, an electric furnace will require assistance from central air conditioning or other sources of cooling comfort.
Heat pump vs air conditioner
Both heat pumps and air conditioners are cooling options, and they share many characteristics.
How are the two systems differ from one another if they operate essentially identically and make use of the same fundamental components? The heat pump is genuinely distinct and unique due to one key component. And this valve allows for direction change.
When the valve is turned, the heat pump will begin to collect heat from the outside rather than the interior.
Your home will become hotter as a result of the heat it accumulates being transferred inside. It is, therefore, a process in reverse. This occurs as a result of the refrigerant's inherent ability to retain the same cycle when operating in reverse.
This way you can utilize a heat pump to heat your house throughout the colder months without having to build another heating system. However it is not suggested that you will just need a heat pump.
Which HVAC system is best for you?
Wondering which HVAC system is right for you? Well, it depends on multiple factors.
a) Purchase & installation costs:
When it comes to inexpensive cooling systems, window-type air conditioners are frequently the first option of the majority of people. However, that despite their lower beginning prices, they nevertheless have astronomically high ongoing expenditures.
The expense of purchasing and installing an indoor and outdoor unit for a heat pump, on the other hand, might be very high. However, since you get a cooler and warmer in one package, it can be taken as a good buy. The best thing is that even though you will have to spend a big chunk initially, you can end up saving a lot in the future.
b) Energy efficiency:
In terms of energy efficiency, heat pumps are considered a better choice. However, both heat pumps and air conditioners have higher SEER ratings.
A heat pump functions effectively and efficiently if you live somewhere where the temperature never drops below freezing. A heat pump won't economical if you live somewhere with really low temperatures, though. The heat pump needed to put more effort when it was too cold, which would raise costs and possibly harm the system.
In this kind of circumstance, utilizing a furnace and an air conditioner together would be less expensive than setting up a heat pump.
c) Longevity of the system:
You should also think about how long the system will last you.
Because you use air conditioners less frequently than heat pumps, they typically last longer.
Air conditioning systems are only utilized during the summer, allowing you to use the furnace throughout the winter.
On the other hand, heat pumps operate throughout the year, which causes them to deteriorate significantly more quickly. However, by making sure that you hire qualified HVAC specialists to tune up your heat pump on a regular basis, you can still significantly extend the lifespan of these systems.
The efficiency of heat pumps is being improved through a number of improvements such as two-speed compressors, variable-speed or dual-speed motors, desuperheaters, scroll compressors, etc.
Think of HVAC system installation and replacements as investments in the comfort of your family. They can be pricey though, so you should make sure you are well-informed about all of your options.
It is strongly advised to speak with an HVAC expert so you can ask any questions you may have in order to make an informed purchase.
How long do heat pumps last?
Heat pumps have an average lifespan of 10 to 15 years because they are frequently used year-round. The two most crucial elements affecting a heat pump's lifespan are how frequently it is operated and whether it got routine maintenance. A regular maintenance schedule for heat pumps should be followed twice a year, once in the spring and in the fall.
At PartsHnC, we provide a wide range of HVAC essential parts. Browse through our catalogue today for your best fit. Parts for HVAC systems from most of the brands are backed by a manufacturer’s warranty. We ship your products same-day to reduce our customer’s waiting times. Reach us at (866) 963-0907 or email us at [email protected] for any queries you have.
 Loyalty Program
Loyalty Program





